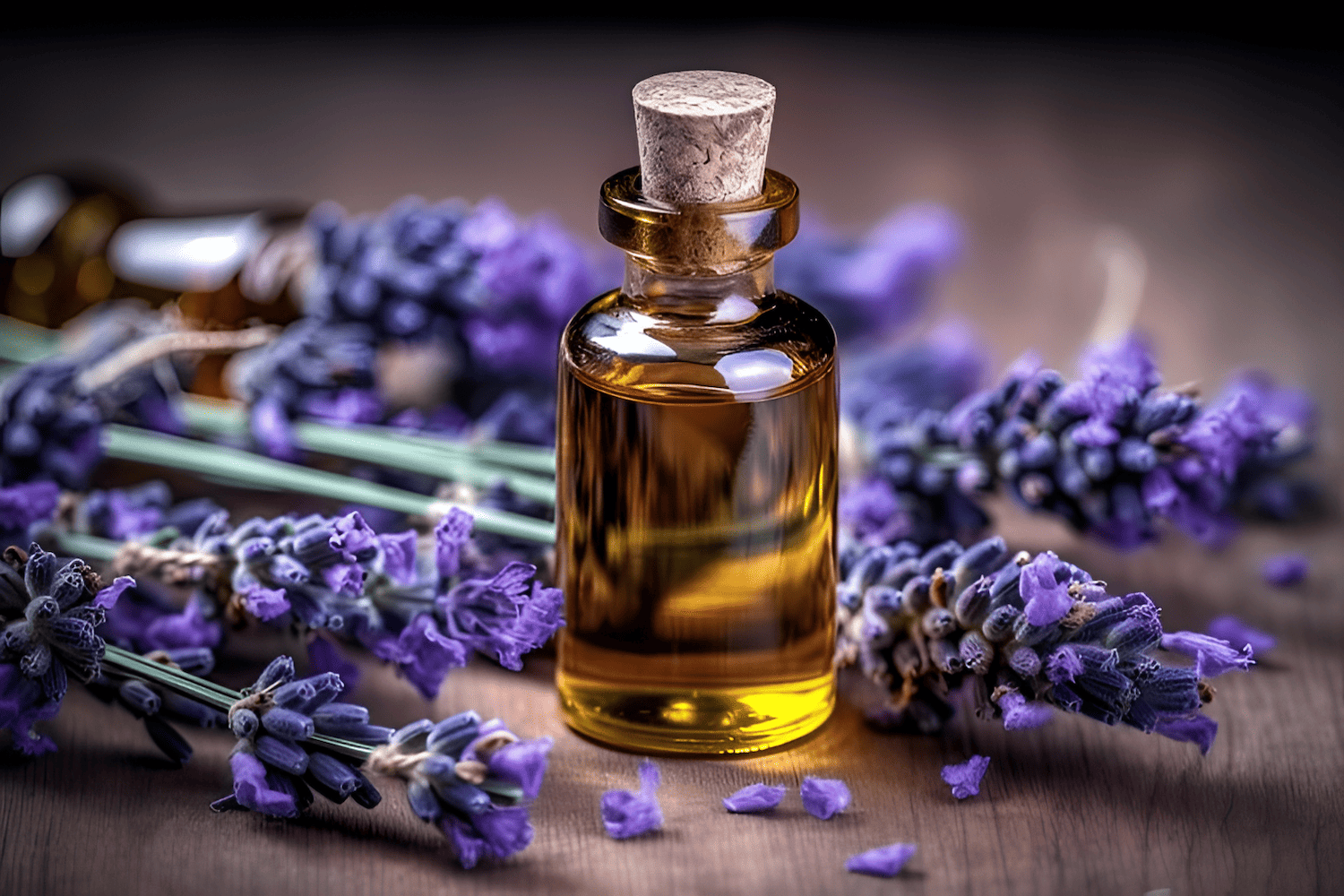
The Allure of Lavender Oil: History, Production, DIY Methods, Uses, and Benefits
Lavender oil, a fragrant and versatile essential oil, has been cherished for centuries for its soothing aroma and myriad of applications. From its historical roots to modern-day uses, we jump into the fascinating world of lavender oil, explaining how it’s made, its benefits, and even how you can create your own at home.Lavender, scientifically known as Lavandula angustifolia, has been a symbol of purity, calmness, and healing since days of yore. The use of lavender dates back over 2,500 years, with its origins traced to the Mediterranean, the Middle East, and India. Ancient Egyptians used lavender in mummification and as perfume, while Greeks and Romans utilized it for bathing, cooking, and as a natural remedy for various ailments.
The name "lavender" comes from the Latin word "lavare," meaning "to wash," reflecting its historical association with cleanliness. During the Renaissance, lavender oil was a popular remedy for the plague, as people believed its strong aroma warded off disease. By the 19th century, the therapeutic properties of lavender were formally recognized, and it became a staple in European households for its calming and antiseptic qualities.